Solvency Ratio Analysis
Solvency Ratio Analysis: It measures the ability of a business to survive for a long period of time. These ratios are very important for stockholders and creditors as these ratios assess the ability of the firm to meet its long-term liabilities.
The solvency ratios are categorized into the following types :
a) Debt Equity Ratio
b) Total Assets to Debt Ratio
c) Proprietary Ratio
d) Interest Coverage Ratio
e) Debt to Capital Employed Ratio
Solvency Ratio – Debt Equity Ratio
It explains the relationship between long-term debts and shareholder funds. The debt-equity ratio of 2:1 is considered ideal.
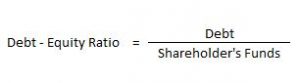
Here, Debt includes Long-term Borrowings and Long-term Provisions. Shareholder’s Funds include Share Capital and Reserve & Surplus.
Solvency Ratio – Total Assets to Debt Ratio
This ratio is a variation of the debt-equity ratio. In this ratio, assets are expressed in terms of long-term debts.
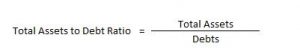
Here, Total Assets = Non- Current Assets + Non-Current Investments + Long Term Loans & Advances + Current Assets
Debts = Long-term Borrowings and Long-term Provisions
Solvency Ratio – Proprietary Ratio
It is the proportion of total assets funded by the shareholders. A higher proprietary ratio is an indicator of sound financial position from a long-term point of view.
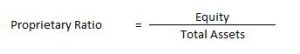
Solvency Ratio – Interest Coverage Ratio
The interest coverage ratio is a debt ratio and profitability ratio used to determine how easily a company can pay interest on its outstanding debt. This ratio indicates how many times the interest charges are covered by the profits available to pay interest charges.

e) Debt to Capital Employed Ratio
This ratio expresses the relation of long-term debt with the sum total of both external and internal funds (i.e., capital employed or net assets).
Debt to capital employed ratio = Long-term Debt/Capital Employed (or Net Assets)
Capital employed can be calculated by taking either the liabilities side or the assets side as the base.
Therefore, it is equal to the long-term debt of the company + shareholders’ funds. Or, it can be calculated by deducting current liabilities from the total assets of the enterprise.
The debt to capital employed ratio depicts the proportion of long term debts forming part of the capital employed. Thus, a lower ratio would provide the lenders with the security of their funds.
Solvency Ratio Examples
How to compute debt-equity ratio – Solvency Ratio Analysis – Question 1
From the following information calculate the debt-equity ratio.
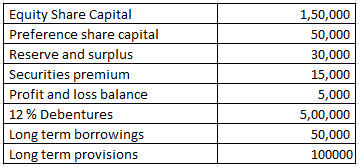
Explanation: –
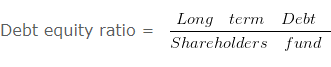
= 650000/250000
= 2.6 : 1
Working note 1 : Long term Debt = 12 % Debentures + Long term borrowings + Long term provisions
Long term Debt = 500000 + 50000 + 100000
Long term Debt = 650000
Working note 2 : Shareholders fund = Equity Share Capital + Preference share capital + Reserve and surplus + Securities premium + Profit and loss balance
Shareholders fund = 150000 + 50000 + 30000 + 15000 + 5000
Shareholders fund = 250000
When total debts are given – Solvency Ratio Analysis – Question 2
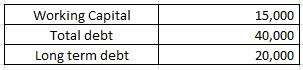
From the following information compute the current ratio.
Explanation : –
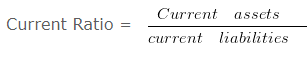
Current Ratio = 35000/20000
Current Ratio = 1.75 :1
Workings:
Working Capital = Current assets (-) Current liabilities
15000 = Current assets (-) 20000
Current assets = 35000
Workings:
Current liabilities = Total debt (-) Long term debt
Current liabilities = 40000 (-) 20000
Current liabilities = 20000
How to compute debt-equity ratio – Solvency Ratio Analysis – Question 3
From the following information calculate the debt-equity ratio.
Explanation : –
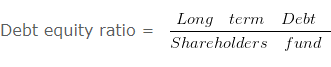
Debt equity ratio = 200000/400000
Debt equity ratio = 0.5 : 1
Working note 1: Long term Debt = Long term borrowings + Long term provisions
Long term Debt = 120000 + 80000
Long term Debt = 200000
Working note 2: Shareholders fund = Noncurrent assets + Working capital (-) Noncurrent liabilities
OR
Shareholders fund = Non current assets + Current assets (-) Current liabilities (-) Long term borrowings (-) Long term provisions
Shareholders fund = 500000 + 200000 (-) 100000 (-) 120000 (-) 80000
Shareholders fund = 400000
Calculation of Equity ratio – Solvency Ratio Analysis – Question 4
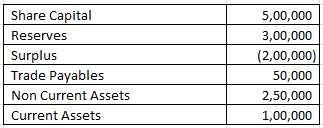
From the Following information calculate Equity Ratio
Explanation : –
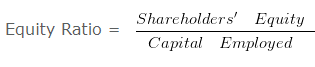
Equity Ratio = 600000/300000
Equity Ratio = 2
Working note 1 :
Shareholders’ Equity = Share Capital + Reserves + Surplus
= 500000 + 300000 + -200000
= 600000
Capital employed = Non Current Assets + Current Assets (-) Trade Payables
Capital employed = 250000 + 100000 (-) 50000
Capital employed = 300000
Calculation of Proprietary Ratio – Solvency Ratio Analysis – Question 5
Compute Proprietary ratio if equity share capital is Rs. 125000, Preference Share Capital is Rs. 100000, Capital Reserve is Rs. 80000, Profit & Loss Balance is Rs. 55000. The value of 7 % Debentures is Rs. 62500 and 9 % Mortgage loan- Rs. 112500. Value of Current Liabilities is Rs. 262500 Non-Current Assets is worth Rs. 275000 Value of Current Assets is Rs. 125000.
Explanation : –
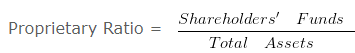
Proprietary Ratio = 360000/400000
Proprietary Ratio = 0.9
Working note 1: Shareholders’ Funds = Equity share capital + Preference share capital + Capital reserve + Profit and loss balance
Shareholders’ Funds = 125000 + 100000 + 80000 + 55000 Shareholders’ Funds = 360000
Working note 2 : Total Assets = Non current assets + Current assets
Total Assets = 275000 + 125000
Total Assets = 400000
Debt to total assets ratio – Solvency Ratio Analysis – Question 6
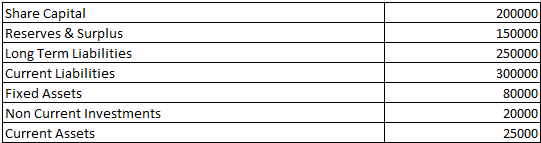
Compute Debt to Total Assets Ratio from the above information.
Explanation : –
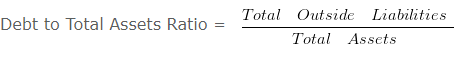
Debt to Total Assets Ratio = 250000/125000
Debt to Total Assets Ratio = 2 :1
Working note 1 :
Total Assets = Fixed Assets + Non Current Investments + Current Assets
= 80000 + 20000 + 25000
Total Assets = 125000
Interest Coverage Ratio – Solvency Ratio Analysis – Question 7
Compute Interest Coverage ratio if equity share capital is Rs. 1200000, Preference Share Capital is Rs. 720000, Capital Reserve is Rs. 360000, Profit & Loss Balance is Rs. 600000. The Value of 13 % debentures is Rs. 250000 and 11 % Mortgage loan of Rs. 300000. The value of Current Liabilities is Rs. 1180000 Non-Current Assets is worth Rs. 2400000 Value of Current Assets is Rs. 3000000.
Explanation : –
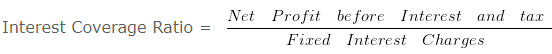
Interest Coverage Ratio = 589500/65500
Interest Coverage Ratio = 9 times
Working Notes:
Interest on debenture = 13% x 250000
= 32500
Interest on loan = 11% x 300000
33000
Total interest charges = 6550
Interest Coverage Ratio & Debt Service Coverage Ratio – Question 8
Calculate- Interest Coverage Ratio & Debt Service Coverage Ratio from the following information. Net Profit before interest and tax is Rs. 300000. 5 % Long Term Debt 500000 (Principle amount is repayable in 10 equal installments) .
Explanation : –
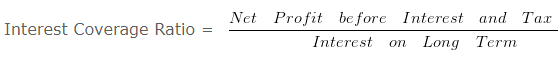
= 300000/25000
= 12 times
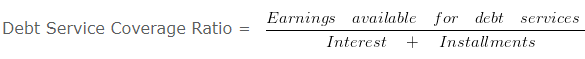
Debt Service Coverage Ratio = 300000/(25000+50000)
Debt Service Coverage Ratio = 300000/75000
Debt Service Coverage Ratio = 4 times
Working Notes:
1. Interest on Long Term Debt = 5 % x 500000
25000
Chapter 5 – Accounting Ratios